توضیحات
ABSTRACT
This work focuses on using machine learning (data analysis) for interpretation and understanding of brainwaves resulting from electroencephalography during a grasping task. Electroencephalography – EEG – was used for acquisition of brain neural signals thought activity, hence to layout a control strategy for robotic hand and fingers movements. This is done via decoding, in real-time, the neural activity associated with fingers motions. Results are used for training robotics dexterous hands, and might allow people with spinal cord injury, rainstem stroke, and ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) to control a robotic-prosthetic by thinking about movements. The project is novel in a sense, it relies on detecting grasping features for a human grasping using Principle Component Analysis (PAC), hence to learn these features for recognitions applications.
INTRODUCTION
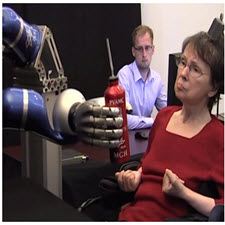
It has been reported clinically that, diseases like stroke and traumatic brain injury do cause long-term, unilateral loss of motor control. Neurological disabilities and related diseases are causing the permanent loss of motoring of limbs, in addition to sensory malfunction. In particular, even in specific and related cases, limbs disability is very severe that it is not likely to feed oneself or even communicate. With the advances ontechnology, and in specific – BMI – Brain Machine Interface, there is a new research direction that aims to support disabled patients by translating neural signals from the brain into useful control signals for guiding prosthetic limbs. The prime objective in developing a neural prosthesis is to substitute neural circuitry in the brain, that no longer functions correctly or efficiently, Fig.1. While achieving such goal, this requires artificial reconstruction of neuron-to neuron connections in a way that can be recognized by the remaining normal circuitry, and that promotes appropriate interaction. It is estimated that approximately (9 million) people worldwide suffer from stroke every year and that almost (30%) of stroke survivors suffering from irreversible motor impairments, Teo et al. . According to Andrew et al., brain-controlled interfaces are devices that capture brain transmissions involved in a subject’s intention to act. Neural activated prosthetic devices is becoming an important domain, and progressively relevant to a number of clinical and various neurological related diseases treatments.
چکیده
این کار تمرکز بر استفاده از یادگیری ماشین (تجزیه و تحلیل داده ها) برای تفسیر و درک موج های مغزی ناشی از الکتروانسفالوگرافی در طول یک کار درک. الکتروانسفالوگرافی – EEG – برای کسب سیگنال های مغز استخوان مغز از فعالیت های ذهنی استفاده شده است، از این رو برای طراحی یک استراتژی کنترل حرکات دست و انگشت رباتیک طراحی شده است. این کار از طریق رمزگشایی، در زمان واقعی، فعالیت عصبی مربوط به حرکات انگشتان دست است. نتایج به دست آمده برای دستکاری دست های رباتیک استفاده می شود و ممکن است افراد با آسیب نخاعی، سکته مغزی، و ALS (اسکلروز جانبی جانبی آمیوتروفی) را برای کنترل یک پروتز روبوتیک با تفکر در مورد حرکات به افراد اجازه دهد. این پروژه به نوعی رمان است و به شناسایی ویژگی های درک برای فهمیدن انسان با استفاده از تجزیه و تحلیل کامپوننت اصل (PAC) کمک می کند، از این رو برای یادگیری این ویژگی ها برای برنامه های تشخیص استفاده می شود.
مقدمه
به طور بالقوه گزارش شده است که بیماری هایی مانند سکته مغزی و آسیب مغزی آسیب می بینند که باعث کاهش طول عمر یک طرفه کنترل حرکت می شوند. ناتوانی های عصبی و بیماری های مرتبط با آن، علاوه بر نقص عملکردی حسی، باعث از دست دادن دائمی موتور در اندام می شود. به طور خاص، حتی در موارد خاص و مرتبط، ناتوانی اندامها بسیار شدید است، زیرا احتمال دارد که آنها غذا یا حتی ارتباط برقرار نکنند. با پیشرفت فن آوری و در ویژه – BMI – مغز ماشین رابط، یک مسیر تحقیق جدید است که هدف آن حمایت از بیماران مبتلا به بیماری با ترجمه سیگنال های عصبی از مغز به سیگنال های کنترل مفید برای هدایت اندام مصنوعی است. هدف اصلی در توسعه یک پروتز عصبی این است که مدار مغز استخوان را در مغز جایگزین کند که دیگر درست یا کارآمد نیست، شکل 1. در حین دستیابی به چنین هدف، این نیاز به بازسازی مصنوعی نورون ها به اتصالات نورونی به گونه ای است که می تواند توسط مدار باقی مانده نرمال شناخته شود و باعث تعامل مناسب می شود. تخمین زده شده است که تقریبا (9 میلیون) نفر در سراسر جهان از سکته مغزی هر سال رنج می برند و تقریبا (30٪) از بازماندگان سکته مغزی از ناراحتی های حرکتی برگشت ناپذیر رنج می برند. . بر طبق گزارش اندرو و همکاران، رابطهای کنترل شده توسط مغز دستگاههایی هستند که انتقال داده های مغزی را درگیر می کنند که در قصد عمل به موضوع وجود دارد. دستگاه های پروتز فعال فعال عصبی در حال تبدیل شدن به یک دامنه مهم هستند و به تدریج به تعدادی از درمان های مختلف مرتبط با بیماری های مرتبط با نوروپاتولوژی مربوط می شوند.
Year: 2018
Publisher : IEEE
By : Ebrahim A. Mattar,Hessa Jassim Al-Junaid
File Information: English Language/ 6 Page / size: 601 KB
سال : 1396
ناشر : IEEE
کاری از : ابراهیم عطاء ماتار، هسا جاسم الجناید
اطلاعات فایل : زبان انگلیسی / 6 صفحه / حجم : KB 601





نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.