توضیحات
ABSTRACT
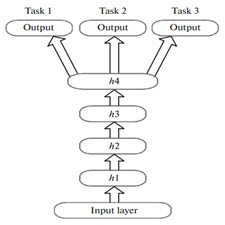
The number of seismological studies based on artificial neural networks has been increasing. However, neural networks with one hidden layer have almost reached the limit of their capabilities. In the last few years, there has been a new boom in neuroinformatics associated with the development of third-generation networks, deep neural networks. These networks operate with data at a higher level. Unlabeled data can be used to pretrain the network, i.e., there is no need for an expert to determine in advance the phenomenon to which these data correspond. Final training requires a small amount of labeled data. Deep networks have a higher level of abstraction and produce fewer errors. The same network can be used to solve several tasks at the same time, or it is easy to retrain it from one task to another. The paper discusses the possibility of applying deep networks in seismology. We have described what deep networks are, their advantages, how they are trained, how to adapt them to the features of seismic data, and what prospects are opening up in connection with their use.
INTRODUCTION
Artificial neural networks (NNs) are widely used for the processing of seismic data (Böse et al., 2008; Gravirov et al., 2012; Lin et al., 2012; Kislov and Gravirov, 2017). It is possible to train the NN to solve such complex tasks as pattern recognition, signal detection, nonlinear modeling, classification, and regression using a training sample in which the correct answer is known for each example (supervised learning). However, the expansion of neural network technologies is constrained by a large number of heuristic rules for network design and training. The main thing is that, in this case, it is never known whether the architecture of the constructed network is optimal or whether it has been trained in the best way, i.e., whether the global minimum of the error function is found. Although an NN with one hidden layer can approximate any function with any accuracy, it can be considered to be a lookup table for the training sample with the more or less correct interpolation of intermediate values and extrapolation at the edges (Cybenko, 1989). The main limitations of the applicability of the NN are also associated with the problems of overfitting, stability-plasticity tradeoff, and the curse of dimensionality (Friedman, 1994). Obviously, different methods are developed to bypass these difficulties, but they are mostly heuristic.
چکیده
تعداد مطالعات زمین شناسی بر اساس شبکه های عصبی مصنوعی افزایش یافته است. با این حال، شبکه های عصبی با یک لایه مخفی تقریبا به حد توانایی های خود رسیده اند. در چند سال گذشته، رونق جدیدی در علوم نوریستی در ارتباط با توسعه شبکه های نسل سوم، شبکه های عصبی عمیق وجود دارد. این شبکه ها با داده ها در سطح بالاتر عمل می کنند. داده های بدون برچسب ممکن است برای پیشگیری از شبکه استفاده شوند، به همین علت، نیازی به متخصص برای پیش بینی پدیده ای است که این اطلاعات با آن مطابقت دارند. آموزش نهایی نیاز به مقدار کمی از داده های برچسب گذاری شده دارد. شبکه های عمیق سطح انتزاعی بیشتری دارند و خطاهای کمتر تولید می کنند. همان شبکه را می توان برای حل چندین وظیفه در یک زمان استفاده کرد، یا آسان است که آن را از یک وظیفه به یک دیگر دوباره مجددا بگذرانیم. مقاله در مورد امکان استفاده از شبکه های عمیق در زلزله شناسی بحث می کند. ما توصیف شده است که شبکه های عمیق، مزایای آنها، چگونگی آموزش آنها، چگونگی تطبیق آنها با ویژگی های داده های لرزه ای، و آنچه که چشم انداز در ارتباط با استفاده از آنها باز می شود، توضیح داده شده است.
مقدمه
شبکه های عصبی مصنوعی (NNs) به طور گسترده ای برای پردازش داده های لرزه ای مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند (Böse et al.، 2008؛ Gravirov et al.، 2012؛ Lin et al.، 2012؛ Kislov and Gravirov، 2017). ممکن است NN آموزش برای حل وظایف پیچیده مانند تشخیص الگو، تشخیص سیگنال، مدل سازی غیر خطی، طبقه بندی و رگرسیون با استفاده از یک نمونه آموزشی که پاسخ صحیح برای هر نمونه (یادگیری نظارت شده) را آموزش دهد. با این حال، گسترش فناوری های شبکه عصبی محدود به تعداد زیادی از قوانین اکتشافی برای طراحی و آموزش شبکه است. نکته اصلی این است که در این مورد، هرگز نمی دانیم که آیا معماری شبکه ساخته شده بهینه است یا اینکه بهترین روش آن آموزش دیده است، یعنی آیا حداقل حداقل تابع خطای یافت شده است. اگر چه یک NN با یک لایه پنهان می تواند هر تابع را با هر دقت متقابل تقریبا نزدیک کند، می توان آن را یک جدول جستجو برای نمونه آموزش با در نظر گرفتن مقادیر متوسط یا مقادیر متوسط و استخراج در لبه ها در نظر گرفت (Cybenko، 1989). محدودیت های اصلی کاربرد NN همچنین با مشکلات بیش از حد تعادل، اعتماد پذیری پلاستیکی و لعن ابعاد همراه است (فریدمن، 1994). بدیهی است، روش های متفاوتی برای جلوگیری از این مشکلات بوجود می آیند، اما اغلب اووریستی هستند.
Year: 2018
Publisher : INC
By : K. V. Kislov and V. V. Gravirov
File Information: English Language/ 9 Page / size: 273 KB
سال : 1396
ناشر : INC
کاری از : K. V. Kislov و V. V. Gravirov
اطلاعات فایل : زبان انگلیسی / 9 صفحه / حجم : KB 273







نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.