توضیحات
چکیده
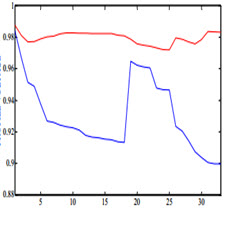
امروزه استفاده از انرژي هاي نو(DG) با توجه بـه ویژگـی هـاي خوب آن در سراسر دنیا روبـه افـزایش مـیباشـد. از ایـن رو مکـان و ظرفیتهاي منابع DGباید عمیقـاً در تلفـات سیسـتم یـک شـبکه توزیـع، نهفته باشند. یکی از مسائل اصلی که در تولیـد تـوان توسـط واحدهاي پراکنده در شبکه هاي توزیع مطـرح اسـت، انتخـاب بهینـه محل و ظرفیت آنها جهـت کـاهش تلفـات و بهبـود پروفیـل ولتـاژ و جلوگیري از افزایش تلفات میباشد. در این مقاله، یک روش ترکیبـی از الگـوریتم ژنتیک و الگـوریتم تبریـد شبیهسازي شده بـراي بهینـه کردن محل و اندازه مطلوب DGدر سیستمهاي توزیـع ارائـه شـده است. هدف به حداقل رساندن تلفات توان شبکه، تنظیم ولتاژ بهتر، و بهبود پایداري ولتاژ در چارچوب عملکرد سیسـتم و محـدودیتهـاي امنیتی در سیستمهاي توزیع شعاعی است. یک آنـالیز دقیـق از ایـن عملکـرد در سیســتم 33باسـه، بــراي نشـان دادن اثربخشــی روش پیشنهادي در مقایسه با روشهاي مرسوم همچون الگـوریتم ازدحـام ذرات، ارائه شده است .
مقدمه
یک سیستم الکتریکی به صورت مجموعهاي شامل سیـستمهـاي تولید، انتقال و سیستم توزیع تقسیم بندي مـیشـود. سـرمایه گـذاري روي دو بخش تولید و توزیـع، در مجمـوع بیشـترین قسـمت از کـل سرمایه شبکه برق را به خود اختصاص میدهـد و از آنجـا کـه مقـدار سرمایه گذاري در بخش توزیع، تقریباً برابر با سرمایه گذاري در بخـش تولید است به همین جهت مـیتـوان فهمیـد کـه سیسـتم توزیـع از اهمیت اقتصادي بسـیار برخـوردار اسـت. بـا توجـه بـه اهمیـت اقتصادي سیستم توزیع و حجم سرمایه گذاري در آن، دقت در طـرح سیستم توزیع امري ضروري میباشد. به طور کلی مسئله طرحریزي، کوششی براي کم کردن هزینه پست ها، فیدرهاي اصـلی و فیـدرهاي فرعی و غیره و نیز کم کردن هزینه اتلافها در سیسـتم توزیـع مـی باشد.
ABSTRACT
Nowadays, the use of new energies (DGs) is increasing due to its good features throughout the world. Therefore, the location and capacity of DG resources should be deeply embedded in the losses of a distribution network system. One of the main issues in power generation by distributed units in distribution networks is the optimal location selection and their capacity to reduce losses and improve the voltage profile and prevent the increase in losses. In this paper, a hybrid method of genetic algorithm and simulated refrigeration algorithm is presented to optimize the optimal location and size of DG in distribution systems. The goal is to minimize network power losses, better voltage regulation, and improve voltage stability within the framework of system performance and security constraints in radial distribution systems. An accurate analysis of this function in the 33 Bass system is presented to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in comparison with conventional methods such as particle swarm algorithm.
INTRODUCTION
An electrical system is divided into a set of production, transmission and distribution systems. Investing in two parts of production and distribution collectively accounts for most of the total capital of the grid, and since the amount of investment in the distribution sector is almost equal to the investment in the manufacturing sector, it can be seen that the system Distribution is of great economic importance. Due to the economic importance of the distribution system and the volume of investment in it, the accuracy of the distribution system design is essential. In general, the design problem is an attempt to reduce the cost of posts, feeders and feeders, etc., as well as reduce the cost of losses in the distribution system.
Year: 2018
Publisher : Third Annual National Conference on Electrical, Computer and Bioelectric Engineering in Iran
By : Abdollah Ebrahimi, Ali Moghimi
File Information: persian Language/ 7 Page / size: 357 KB
Only site members can download free of charge after registering and adding to the cart
سال :1397
ناشر : سومین کنفرانس سالانه ی ملی مهندسی برق ,کامپیوتر و بیوالکتریک ایران
کاری از : عبداله ابراهیمی ،علی مقیمی
اطلاعات فایل : زبان فارسی / 7 صفحه / حجم : KB 357







نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.