توضیحات
ABSTRACT
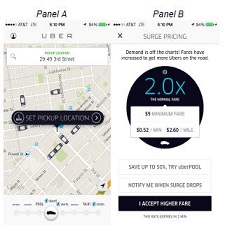
Estimating consumer surplus is challenging because it requires identification of the entire demand curve. We rely on Uber’s “surge” pricing algorithm and the richness of its individual level data to first estimate demand elasticities at several points along the demand curve. We then use these elasticity estimates to estimate consumer surplus. Using almost 50 million individuallevel observations and a regression discontinuity design, we estimate that in 2015 the UberX service generated about $2.9 billion in consumer surplus in the four U.S. cities included in our analysis. For each dollar spent by consumers, about $1.60 of consumer surplus is generated. Back-of-the-envelope calculations suggest that the overall consumer surplus generated by the UberX service in the United States in 2015 was $6.8 billion
INTRODUCTION
For over 250 years, economists have recognized the importance of consumer surplus when making welfare calculations.2 Consumer surplus (and the closely related concepts of equivalent variation and compensating variation) is a critical input to many economic policies, such as antitrust analysis, the valuation of non-market goods, and measuring the value of innovation(e.g., Williamson 1968, Willig 1976, Bresnahan 1986). In practice, however, obtaining convincing empiricalestimates of consumer surplus has proven to be extremely challenging. We typically observe only the equilibrium point that balances supply and demand. Variations in that equilibrium across time and space are generally the result of a combination of supply-driven and demand-driven shocks and thus are of little use in this regard. A large body of economic research focuses on demand estimation (see, for instance, Deaton 1986). The key to estimating demand elasticities is to isolate exogenous shifts in the supply curve, holding demand factors constant. In recent years, a great deal of work has focused on the development of new techniques for generating demand estimates in differentiated product markets (Baker and Bresnahan 1988, Berry et al. 1995, Nevo 2000, Petrin 2002).3 This strand of the literature focuses on overcoming the data limitations that are often present in standard economic settings, such as the absence of individual level data, unobservable product
characteristics, and unobservable consumer characteristics
Year : 2016
By : Peter Cohen, Robert Hahn, Jonathan Hall,Steven Levitt, and Robert Metcalfe
File Information : English Language / 42 Page /Size : 3.9 M
Download : click
سال : 2016
کاری از : Peter Cohen, Robert Hahn, Jonathan Hall,Steven Levitt, and Robert Metcalfe
اطلاعات فایل : زبان انگلیسی /42 صفحه / حجم : 3.89 M
لینک دانلود : روی همین لینک کلیک کنید






نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.