توضیحات
ABSTRACT
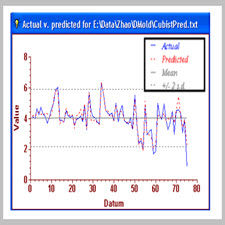
The paper describes a novel, user friendly integrated data mining system which can be used by users to analyse in-house commercially sensitive toxicity data sets. The system provides a unified userinterface and environment in a way that users can be freed from time-consuming data transformation and exchange between tools, pre-processing and preparation as well as tool selection. The system has the following components: a data input module which allows data to be input into the system in various forms including flat files, Excel, Access, and XML; pre- processing for missing value handling, outlier identification and removal, scaling, noise removal, feature extraction, data compression, dependence and correlation analysis; a data mining module including various supervised and unsupervised tools, such as neural and statistical based approaches, dependency modelling and inductive learning for decision tree and rule generation; as well as multidimensional visualisation such as parallel coordinates. Some of the tools are not available in existing commercial systems. It also includes a module for calculation of molecular descriptors, and a separate module for mixture toxicity prediction using a new approach. The functionality of the system will be demonstrated using case studies.
INTRODUCTION
Each year thousands of chemicals are released into the environment for which little or nothing is known about their potential toxicity (Basak et al., 2003, Lee et al., 1998, Ren and Schultz, 2002). In conjunction with the ever-increasingly stringent environmental regulation, according to the specialised organic chemicals sector association (SOSCA) in the UK, environmental management has in recent years become the dominant cost factor for many specialty chemicals manufactured in the U.K., representing around 16% of the total turnover (DEFRA, 2002). Currently, toxicity is assessed by expensive and time-consuming tests usually costing between $2,000 and $2,000,000 and lasting from 15 to 730 days (Smith, 2000) often using animal assays, which are increasingly viewed negatively by the general public (Ridings et al., 1996). More importantly, such tests cannot be carried out before the chemicals, usually in the form of waste effluents, are actually produced.
Year: 2002
PublisheK:LS2, U, 9JT,
By: Frances V Buontempo, Nigel Horan, Anita Youngv, Daniel Osborn
File Information: English Language/ 9 Page / size:150KB
Download: click
سال : 2002
ناشر :LS2, U, 9JT
کاری از : Frances V Buontempo, Nigel Horan, Anita Youngv, Daniel Osborn
اطلاعات فایل : زبان انگلیسی / 9 صفحه / حجم : 150KB
لینک دانلود : روی همین لینک کلیک کنید







نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.