توضیحات
ABSTRACT
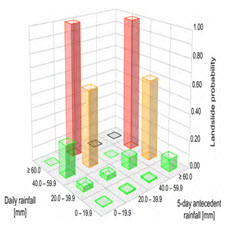
Researchers have long attempted to determine the amount of rainfall needed to trigger slope failures, yet relatively little progress has been reported on the effects of climate change on landslide initiation. Indeed, some relationships between landslides and climate change have been highlighted, but sign and magnitude of this correlation remain uncertain and influenced by the spatial and temporal horizon considered. This work makes use of statistically adjusted high-resolution regional climate model simulations, to studythe expected changes of landslides frequency in the eastern Esino river basin CentralItaly). Simulated rainfall was used in comparison with rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrence derived by two observation-based statistical models (1) the cumulative event rainfall–rainfall duration model, and (2) the Bayesian probabilistic model. Results show an overall increase in projected landslide occurrence over the twenty-first century. This is especially confirmed in the high-emission scenario representative concentration pathway 8.5, where according to the first model, the events above rainfall thresholds frequency shift from * 0.025 to * 0.05 in the mountainous sector of the study area. Moreover, Bayesian analysis revealed the possible occurrence of landslide-triggering rainfall with a magnitudenever occurred over the historical period. Landslides frequency change signal presents also
considerable seasonal patterns, with summer displaying the steepest positive trend coupled to the highest inter-model spread. The methodological chain here proposed aims at representing a flexible tool for future landslide-hazard assessment, applicable over different areas and time horizons (e.g., short-term climate projections or seasonal forecasts).
INTRODUCTION
Over the next decades, societies will face massive environmental changes potentially able to substantially alter life styles and priorities (Lenton et al. 2008). Climate change will possibly be the major driver of such changes. However, if on the one hand the scientific community unequivocally recognized over these past decades the connection between the increase in greenhouse gases (GHGs) concentration and the increase in global temperature (Bindoff et al. 2013), on the other hand, changes in the rainfall patterns as a second-order effect of the increased temperature is connoted by higher uncertainty. Such reservations concern the magnitude and frequency of extreme events, how they will scale across the globe in response to the increase in temperature (Seneviratne et al. 2012; Scoccimarro et al. 2013; Drobinski et al. 2016).
چکیده
محققان مدتها تلاش کرده اند مقدار باران مورد نیاز برای ایجاد ناپایداری شیب را تعیین کنند، با این حال هنوز در مورد اثرات تغییرات آب و هوایی بر روی شروع زمستان لغزش گزارش شده است. در واقع، برخی از روابط بین زمين لغزش ها و تغییرات آب و هوایی مشخص شده است، اما نشانه و بزرگی این همبستگی هنوز نامشخص است و تحت تاثیر افق های فضایی و زمانی قرار گرفته است. این کار استفاده از شبیه سازی مدل های آب و هوایی محلی با تفکیک آماری بالا را برای مطالعه تغییرات پیش بینی شده در فرکانس های زمینی لغزش در حوضه ی رودخانه ایسینو مرکزی ایتالیا مورد استفاده قرار می دهد. بارندگی شبیه سازی شده در مقایسه با آستانه بارندگی برای رخداد زمینی لغزش، حاصل از دو مدل آماری مبتنی بر مشاهدات (1) مدل زمان بارش بارندگی و بارندگی تجمعی و (2) مدل احتمالاتی بیزی است. نتایج نشان می دهد که افزایش کلی در پیش بینی وقوع زمینی لغزش در قرن بیست و یکم. این به ویژه در مسیر انبساط 8.5 نشانگر سناریو با شدت تأیید، که در آن طبق مدل اول، وقایع بالای آستانه بارندگی بار از 0.025 تا 0.05 در بخش کوهستانی منطقه مطالعه تغییر می کند. علاوه بر این، تجزیه و تحلیل بیزی نشان داد که احتمال وقوع بارش بارندگی زمینی لغزش در طول دوره تاریخی رخ داده است. سیگنال تغییر فرکانس زمینلغزش همچنین الگوهای قابل توجه فصلی را ارائه می دهد که تابستان با آن رو به رو می شود که سریعترین روند مثبت را به بالاترین سطح بین الملل مرتبط می کند. زنجیره روش شناسی در اینجا پیشنهاد شده است که نشان دهنده یک ابزار انعطاف پذیر برای ارزیابی خطر زمینی لغزش است که در مناطق مختلف و افق های زمانی کاربرد دارد (مثلا طرح های آب و هوایی کوتاه مدت یا پیش بینی های فصلی).
مقدمه
در دهه های بعدی، جوامع با تغییرات گسترده زیست محیطی مواجه خواهند شد که به طور بالقوه قادر به تغییر سبک های زندگی و اولویت های اساسی است (لنتون و همکاران 2008). تغییرات آب و هوایی احتمالا یکی از محرک اصلی این تغییرات خواهد بود. با این حال، اگر از یک سو جامعه علمی در دهه های گذشته به طور واضح شناخته شده است، ارتباط بین افزایش غلظت گازهای گلخانه ای (GHG) و افزایش دمای جهانی (Bindoff و همکاران 2013)، از سوی دیگر، تغییر در الگوهای بارندگی به عنوان اثر درجه دوم درجه حرارت افزایش می یابد با عدم قطعیت بالاتر. چنین احتمالی مربوط به میزان و فرکانس حوادث شدید است، چگونه در پاسخ به افزایش دما در سراسر جهان مقیاس می شوند (Seneviratne et al. 2012؛ Scoccimarro et al. 2013؛ Drobinski et al.، 2016).
Year: 2018
Publisher : SPRINGER
By : Lorenzo Sangelantoni,Eleonora Gioia,Fausto Marincioni
File Information: English Language/ 36 Page / size: 1.06 MB
سال : 1396
ناشر : SPRINGER
کاری از : Lorenzo Sangelantoni، Eleonora Gioia، Fausto Marincioni
اطلاعات فایل : زبان انگلیسی / 36 صفحه / حجم : MB 1.06






نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.