توضیحات
ABSTRACT
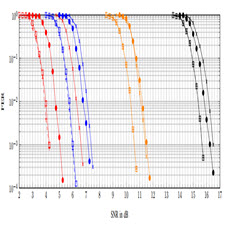
A flexible incremental redundancy hybrid automated repeat request (IR-HARQ) scheme for polar codes is proposed based on dynamically frozen bits and the quasi-uniform puncturing (QUP) algorithm. The length of each transmission is not restricted to a power of two. It is applicable for the binary input additive white Gaussian noise (biAWGN) channel as well as higher-order modulation. Simulation results show that this scheme has similar performance as directly designed polar codes with QUP and outperforms LTE-turbo and 5G-LDPC codes with IR-HARQ.
INTRODUCTION
Many communication channels are time-varying and unknown to the transmitter. Incremental redundancy hybrid automated repeat request (IR-HARQ) as shown in Fig. 1 is a scheme that transmits additional redundancy bits until the data bits can be reconstructed. For turbo codes (such as those used in LTE), a low rate mother code is punctured with different patterns for several transmissions. The coding scheme for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) in 5G uses protographbased, Raptor-like LDPC codes that allow for both flexible block length and code rate adaptation. The standard defines two base matrices that offer optimized performance for different operating regimes. With cyclic redundancy check (CRC) outer codes and successive cancellation list (SCL) decoding , polar codes outperform state-of-the-art turbo and LDPC codes in the short to medium length regime. Polar-coded modulation (PCM) is discussed in . The performance comparison and efficient code design methods of three polar-coded modulation schemes are presented in [8, Fig. 11]. Multilevel polar coding (MLPC) with set partitioning (SP) labeling in performs best and is around 1 dB more power efficient than an AR4JA LDPC code decoded with 200 iterations.
چکیده
الگوریتم تکاملی شبه یکنواخت (QUP) بر اساس بیت های پویا یخ زده پیشنهاد شده (IR-HARQ) برای کد های قطبی یک برنامه انحصاری افزایشی انعطاف پذیر افزوده شده است. طول هر انتقال به قدرت دو محدود نمی شود. این برای کانال گاوسی سفید افزایشی ورودی باینری (biAWGN) و نیز مدولاسیون بالاتر نظیر است. نتایج شبیه سازی نشان می دهد که این طرح عملکرد مشابهی با کدهای قطبی مستقیم با QUP دارد و بهتر است از کد های LTE-turbo و 5G-LDPC با IR-HARQ استفاده شود.
مقدمه
بسیاری از کانال های ارتباطی متغیر هستند و به فرستنده ناشناخته هستند. همانطور که در شکل 1 نشان داده شده است، درخواست تکرار خودکار (IR-HARQ) کارآیی افزایشی اضافه شده است که یک بیت اضافی را بارگذاری می کند تا بیت های داده ها بتوانند بازسازی شوند. برای کدهای توربو (مانند آنچه که در LTE استفاده می شود)، کد مادر پایین با الگوهای مختلف برای چندین انتقال پر شده است. طرح کدگذاری برای افزایش پهنای باند تلفن همراه (eMBB) در 5G از کد های LDPC مانند پروتکل متفاوتی مانند Raptor استفاده می کند که برای طول بلوک انعطاف پذیر و سازگاری با نرخ کد امکان پذیر است. این استاندارد دو ماتریس پایه را تعریف می کند که عملکرد مطلوب را برای رژیم های عملیاتی مختلف ارائه می دهند. با استفاده از رمزگذاری بیرونی چرخه کار (CRC) و رمزگشایی (SCL) رمزنگاری پیوسته، کد های قطبی از کورس های پیشرفته تربو و LDPC در رژیم کوتاه تا متوسط طولانی تر عمل می کنند. مدولاسیون قطبی کد (PCM) در مورد بحث شده است. مقایسه عملکرد و روش های کارآمد طراحی کد از سه طرح مدولاسیون کدگذاری قطبی در [8، شکل 11] ارائه شده است. کد گذاری چند قطبی قطبی (MLPC) با برچسب بندی پارتیشن بندی (SP) در بهترین حالت انجام می شود و در حدود 1 دسیبل بیشتر کارآیی بیشتری نسبت به یک کد LDPC AR4JA با 200 تکرار رمزگذاری شده است.
Year: 2018
Publisher : IEEE
By : Peihong Yuan, Fabian Steiner, Tobias Prinz, Georg Bocherer
File Information: English Language/ 6 Page / size: 136 KB
سال : 1396
ناشر : IEEE
کاری از : پیونگ یوان، فابیان استینر، توبیاس پرینس، گرگ بوچر
اطلاعات فایل : زبان انگلیسی / 6 صفحه / حجم : KB 136




![The Electricity Situation in Ghana[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/The-Electricity-Situation-in-Ghanataliem.ir_.jpg)


نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.