توضیحات
ABSTRACT
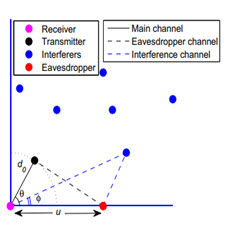
In this paper, we study the receiver performance with physical layer security in a Poisson field of interferers. We compare the performance in two deployment scenarios: (i) the receiver is located at the corner of a quadrant, (ii) the receiver is located in the infinite plane. When the channel state information (CSI) of the eavesdropper is not available at the transmitter, we calculate the probability of secure connectivity using the Wyner coding scheme, and we show that hiding the receiver at the corner is beneficial at high rates of the transmitted codewords and detrimental at low transmission rates. When the CSI is available, we show that the average secrecy capacity is higher when thereceiver is located at the corner, even if the intensity of interferers in this case is four times higher than the intensity of interferers in the bulk. Therefore boundaries can also be used as a secrecy enhancement technique for high data rate applications.
INTRODUCTION
With the forecasted deployment of indoor ultra-dense wireless networks, it becomes important to develop models that consider the impact of boundaries in the performance analysis. It is well-known that close to the boundary, the connection probability degrades due to isolation, but it improves in terms of interference . Analytical models considering finite deployment areas have so far been used to study spatial and temporal interference aspects optimize the base station density in cellular networks , assess millimeter-wave network performance, etc. Physical layer security (PLS) without exchanging secret keys was first proposed by Wyner , and refers to the protection of information messages against eavesdropping with the aid of channel coding. PLS would be well-suited for devices with light computational power, e.g., in certain types of sensor networks, where conventional security techniques fail . Nevertheless, the impact of boundaries on connectivity and rate with PLS has so far received limited attention.
چکیده
در این مقاله، عملکرد گیرنده را با امنیت لایه فیزیکی در میدان مزاحم پوآسون بررسی می کنیم. ما عملکرد را در دو سناریوی استقرار مقایسه می کنیم: (i) گیرنده در گوشه ای از یک ربع قرار دارد؛ (ii) گیرنده در هواپیما بی نهایت واقع شده است. هنگامی که اطلاعات مربوط به کانال وضعیت (CSI) اسرار پیمان در فرستنده موجود نیست، احتمال اتصال اتصال ایمن را با استفاده از طرح کدگذاری Wyner محاسبه می کنیم و نشان می دهیم که پنهان کردن گیرنده در گوشه ای با نرخ های بالا از کلمات کدونی انتقال یافته سودمند است و مضر در نرخ انتقال کم است. هنگامی که CSI در دسترس است، ما نشان می دهیم که ظرفیت محرمانگی متوسط زمانی بالاتر است که گیرنده در گوشه قرار بگیرد، حتی اگر شدت تداخل در این مورد چهار برابر بیشتر از شدت تداخل در حجم باشد. بنابراین، مرزها همچنین می توانند به عنوان یک روش تقویت محرمانه برای برنامه های کاربردی با سرعت بالا استفاده شوند.
مقدمه
با پیش بینی استفاده از شبکه های بی سیم داخلی فوق العاده متراکم، برای توسعه مدل هایی که تاثیر مرزها در تجزیه و تحلیل عملکرد را در نظر می گیرند، مهم است. به خوبی شناخته شده است که نزدیک به مرز، احتمال اتصال به دلیل انزوا کاهش می یابد، اما از لحاظ تداخل بهبود می یابد. مدل های تحلیلی با توجه به نقاط ورودی محدود، تاکنون مورد استفاده قرار گرفته اند تا جنبه های دخالت فضایی و زمانی را بهینه کنند، تراکم ایستگاه پایه در شبکه های تلفن همراه، ارزیابی عملکرد شبکه های میلیمتری و غیره. امنیت لایه فیزیکی (PLS) بدون تغییر کلید های مخفی ابتدا توسط Wyner پیشنهاد شد و به حفاظت از پیام های اطلاعاتی علیه استراق سمع با کمک برنامه نویسی کانال اشاره دارد. PLS برای دستگاه هایی با توان محاسباتی نور مناسب است، مثلا در انواع خاصی از شبکه های حسگر، که در آن روش های امنیتی معمول شکست . با این وجود، تاثیر محدودیت ها در اتصال و نرخ با PLS تا به حال توجه محدود شده است.
Year: 2018
Publisher : IEEE
By : Konstantinos Koufos and Carl P. Dettmann
File Information: English Language/ 13 Page / size: 325 KB
سال : 1396
ناشر : IEEE
کاری از : کنستانتینوس کوفس و کارل پتی Dettmann
اطلاعات فایل : زبان انگلیسی / 13 صفحه / حجم : KB 325



![DAMAGE DETECTION OF STRUCTURES UNDER EARTHQUAKE[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/DAMAGE-DETECTION-OF-STRUCTURES-UNDER-EARTHQUAKEtaliem.ir_.jpg)




نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.