توضیحات
چکیده
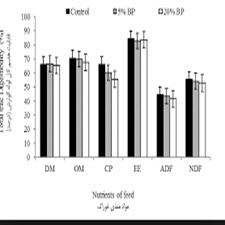
این پژوهش به منظور مطالعه اثر سطوح مولتی آنزیم و سطوح افزودنی باکتریایی بر ترکیب شیمیاییو برخی فراسنجه های تخمیر برون تنی سیلاژ جو انجام شد. مولتی آنزیم روابیو در سه سطح صفر، 500 و1000 میلی گرم به ازای هر کیلو گرم ماده خشک و افزودنی باکتریایی پروسیج (مخلوطی از باکتری های لاکتوباسیلوس پلانتاروم، لاکتوباسیلوس بوچنری، انتروکوکوس فائوسیوم و پروپیونوباکتریوم اسیدوفیلوس) در سه سطح صفر، پنج و 10 میلی گرم به ازای هر کیلوگرم ماده خشک سیلاژ جو استفاده شد. ترکیب شیمیایی، فراسنجه های تولید گاز و جمعیت پروتوزوآ در شرایط برون تنی و بخش های مختلف پروتئین خام سیلاژهای آزمایشی اندازه گیری شد. نتایج نشان داد که افزودن مولتی آنزیم باعث کاهش الیاف نامحلول در شوینده خنثی (05/0> P) pH، خاکستر، پروتئین قابل حل در شوینده خنثی و پروتئین غیرقابل دسترس (01/0> P) و افزایش نیتروژن غیرپروتئینی و پروتئین غیرقابل حل در شوینده خنثی (01/0> P) نسبت به سیلاژ شاهد شد. سیلاژ جو حاوی 5 میلی گرم افزودنی باکتریایی ماده خشک، pH و پروتئین قابل حل در شوینده خنثی بیش تر (01/0> P) و پروتئین غیرقابل دسترس کمتری (01/0> P) در مقایسه با سیلاژ شاهد و سیلاژ جو حاوی 10 میلی گرم افزودنی باکتریایی داشت. جمعیت پروتوزوآ، غلظت نیتروژن آمونیاکی، انرژی قابل متابولیسم، اسیدهای چرب کوتاه زنجیر و قابلیت هضم ماده آلی با روش برون تنی تحت تاثیر قرار نگرفت (05/0<P). بر اساس نتایج این آزمایش استفاده از افزودنی باکتریایی و مولتی آنزیم در تهیه سیلاژ جو پژمرده شده به خاطر بار مالی که می تواند ایجاد کند، توصیه نمی شود.
ABSTRACT
This study was conducted to study the effect of multi enzyme levels and bacterial additive levels on chemical composition and some barley fermentation parameters of barley silage. Multi-enzyme Rubio at three levels of 0, 500 and 1000 mg per kg of dry matter and bacterial perchaeg (a mixture of Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus boucnari, Enterococcus faecium and Propionobacterium acidophilus) at three levels of zero, five and 10 mg For each kilogram of dry matter, barley silage was used. The chemical composition, gas production and protozoa populations were measured in exogenous conditions and different parts of the crude protein of the experimental silages. The results showed that the addition of multi enzyme reduced the insoluble fiber content in neutral detergent (P <0.05) pH, ash, soluble protein in neutral detergent and inaccessible protein (P <0.01), and increased non-protein nitrogen and insoluble protein In neutral detergent (P <0.01), it was seen as silage. Barley slurry contains 5 mg of bacterial additive, dry matter, pH and soluble protein in neutral detergent (P <0.01) and inaccessible protein (P <0.01) compared to control silage and barley silage containing 10 Mg of bacterial additive. The protozoal population, ammonia nitrogen concentration, metabolizable energy, short chain fatty acids, and organic matter digestibility were not affected by exogenous methods (P <0.05). Based on the results of this experiment, the use of bacterial and multi-enzyme additives in the preparation of posed barley silage is not recommended due to the financial burden that can be caused.
Year: ۲۰۱۹
Publisher : Quarterly journal of animal production, Volume
By : Asma Absalan, Golnaz Ozasli, Shahriar Kargar, Farshid Fattahnia, Zohreh Kosar, Alidad Bostani
File Information: English Language/ 12 Page / size: 712 KB
Only site members can download free of charge after registering and adding to the cart
سال : ۱۳۹۸
ناشر : فصلنامه تولیدات دامی، دوره
کاری از : اسماء آبسالان ,گلناز تأسلی ،شهریار کارگر ,فرشید فتاح نیا ،زهره کوثر ،علیداد بوستانی
اطلاعات فایل : زبان فارسی / 12 صفحه / حجم : KB 712







نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.