![A self-organized structure for mobility management in wireless[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/A-self-organized-structure-for-mobility-management-in-wirelesstaliem.ir_.jpg)
A self-organized structure for mobility management in wireless networks
اطلاع رسانیThe objective of this work is to analyse performance of unstable mobile nodes with selforganization structures in Delay Tolerant Networks (DTN). This process enables the nodes to utilize their power fairly, and ensures that the links are established between nodes and used to improve the connectivity. In this paper two approaches are proposed: 1. Self-Healing (SH) and 2. Unstable Topology Structure (UTS) approaches based on localized computations. The proposed work is proven with simulations by analysing node degree, coverage area and Quality of Service (QoS) parameters. The performance of the work is analysed in a network simulator with mathematical models.
![A New Battery Charger for Plug-in Hybrid[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/A-New-Battery-Charger-for-Plug-in-Hybridtaliem.ir_.jpg)
A New Battery Charger for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Application using Back to Back Converter in a Utility Connected Micro-grid
اطلاع رسانیThe major drawbacks of the most battery chargers for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) are high volume and weight, low power, long charging time, deleterious harmonic effects on the electric utility distribution systems and low flexibility and reliability. This paper proposes a new battery charger structure for PHEV application using back to back (B2B) converter in a utility connected micro-grid. In the proposed structure, an AC micro-grid, based on the typical household circuitry configuration, is connected to the grid via a B2B converter; and the DC link is used for battery charging. In fact, the B2B converter can provide an isolated, low cost, simple and reliable connection with power-flow management between the grid, micro-grid and battery. This proposed structure, depending on the power requirement of the vehicle, can run in four different modes: battery charging mode from the grid (G2V) or microgrid (M2V), vehicle to grid mode (V2G) and vehicle to micro-grid mode (V2H). The feasibility of the proposed scheme has been validated in the simulation study for various operating conditions.
![Reactive Power Generation Management for the[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/Reactive-Power-Generation-Management-for-thetaliem.ir_.jpg)
Reactive Power Generation Management for the Improvement of Power System Voltage Stability Margin
اطلاع رسانیVoltage stability margin (VSM) of the power system relates to the reactive power reserves in the network. This paper presents a method to improve the VSM by generator reactive power generation rescheduling. The management of the var generation formulated as an optimization problem and pseudo-gradient evolutionary programming (PGEP) was used to obtain the optimal solution. Modal analysis technique was used to guide the searching direction. Simulation results on the New England 39-bus system demonstrate that the proposed method is effective. Compared with the standard evolutionary programming (SEP), better solution can be obtained, and the convergence speed of the algorithm is improved also. The simulation results show that after the optimal reactive power rescheduling the reactive power reserves of the system is increased and the active/reactive power losses are decreased. The most important advantage is that, the voltage stability margin of power system can be improved without adding new var compensation equipment and changing the active power distribution.
![Modeling of Sediment Management for the Lavey[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/Modeling-of-Sediment-Management-for-the-Laveytaliem.ir_.jpg)
Modeling of Sediment Management for the Lavey Run-of-River HPP in Switzerland
اطلاع رسانیReservoir sedimentation hinders the operation of the Lavey run-of-river hydropower plant (HPP) on the Rhone River in Switzerland. Deposits upstream of the gated weir and the lateral water intake reduce the flood release capacity and entrain sediments into the power tunnel. Past flushing operations of the relatively wide and curved reservoir have been inefficient. To improve sediment management, the enhanced scheme Lavey+ with an additional water intake and a training wall for improving flushing was set up. The performance of the enhancement project was tested on a physical model. For its calibration, sediment transport, deposition, and flushing of the present scheme were investigated and compared with prototype measurements. The enhanced scheme was then analyzed in detail to define the flushing discharge and duration, and define the gate operation to ensure maximal erosion of deposits with minimal water loss.
![Towards A Scalable Scientific Data Grid Model and Services[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/Towards-A-Scalable-Scientific-Data-Grid-Model-and-Servicestaliem.ir_.jpg)
Towards A Scalable Scientific Data Grid Model and Services
اطلاع رسانیScienti fic Data Grid mostly deals with large computational problems. It provides geographically distributed resources for large-scale data-intensive applications that generate large scienti fic data sets. This required the scientist in modern scienti fic computing communities involve in managing massive amounts of a very large data collections that geographically distributed. Research in the area of grid has given various ideas and solutions to address these requirements. However, nowadays the number of participants (scientists and institutes) that involve in this kind of environment is increasing tremendously. This situation has leads to a problem of scalability. In order to overcome this problem we need a data grid model that can scale well with the increasing of user. Peer-to-peer (P2P) is one of the architecture that promising scale and dynamism environment. In this paper, we present a P2P model for Scienti fic Data Grid that utilizes the P2P services to address the scalability problem. By using this model, we study and propose various decentralized discovery strategies that intend to address the problem of scalability. We also investigate the impact of data replication that addressing the data distribution and reliability problem for our Scientific Data Grid model on the propose discovery strategies.
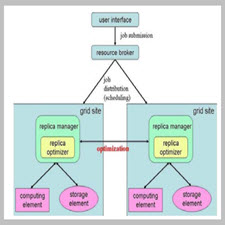
Job Scheduling for Dynamic Data Replication Strategy in Heterogeneous Federation Data Grid Systems
اطلاع رسانیData grid technology has the advantage of allowing data sharing and collaboration activities across many organizations in geographically dispersed locations. Due to collaboration activities in distributed data grid, improving data access is one of the issues that need to be wisely addressed in achieving better optimization. In this paper, a replication model for federation data grid system called Sub-Grid-Federation hadbeen proposed to improve access latency by accessing data from an area identified as ‘Network Core Area’ (NCA). The performance of access latency in Sub-Grid-Federation had been tested based on the mathematical proving and simulated using OptorSim simulator. Hence, Sub-Grid-Federation is a better alternative for the implementation of collaboration and data sharing in data grid system .
![A Taxonomy of Data Scheduling in Data Grids and Data Centers Problems and[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/A-Taxonomy-of-Data-Scheduling-in-Data-Grids-and-Data-Centers-Problems-andtaliem.ir_.jpg)
A Taxonomy of Data Scheduling in Data Grids and Data Centers: Problems and Intelligent Resolution Techniques
اطلاع رسانیScheduling in traditional distributed systems has been mainly studied for system performance parameters without data transmission requirements. With the emergence of Data Grids (DGs) and Data Centers, data-aware scheduling has become a major research issue. DGs arise quite naturally to support needs of scientific communities to share, access, process, and manage large data collections geographicallydistributed. In fact, DGs can be seen as precursors of Data Centers of Cloud Computing platforms, which serve as basis for collaboration at large scale. In such computational infrastructures, the large amount of data to be efficiently processed is a real challenge. One of the key issues contributing to the efficiency of massive processing is the scheduling with data transmission requirements. Data-aware scheduling, although similar in nature with Grid scheduling, is giving rise to the definition of a new family of optimization problems. New requirements such as data transmission, decoupling of data from processing, data replication, data access and security are the basis for the definition of a whole axonomy of data scheduling problems from an optimization perspective. In this work we present the modelling of such requirements and define data scheduling problems. We exemplify the methodology for the case of data-ware independent batch task scheduling and present several heuristic resolution methods for the problem.
![Application of Association Rule Mining for[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/Application-of-Association-Rule-Mining-fortaliem.ir_.jpg)
Application of Association Rule Mining for Replication in Scientific Data Grid
اطلاع رسانیGrid computing is the most popular infrastructure in many emerging field of science and engineering where extensive data driven experiments are conducted by thousands of scientists all over the world. Efficient transfer and replication of these peta-byte scale data sets are the fundamental challenges in Scientific Grid. Data grid technology is developed to permit data sharing across many organizations in geographically disperse locations. Replication of data helps thousands of researchers all over the world to access those data sets more efficiently. Data replication is essential to ensure data reliability and availability across the grid. Replication ensures above mentioned criteria by creating more copies of same data sets across the grid. In this paper, we proposed a data mining based replication to accelerate the data access time. Our proposed algorithm mines the hidden rules of association among different files for replica optimization which proves highly efficient for different access patterns. The algorithm is simulated using data grid simulator, OptorSim, developed by European Data Grid project. Then our algorithm is compared with the existing approaches where it outperforms others.
![Chameleon A Resource Scheduler in A Data Grid Environment[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/Chameleon-A-Resource-Scheduler-in-A-Data-Grid-Environmenttaliem.ir_.jpg)
Chameleon: A Resource Scheduler in A Data Grid Environment
اطلاع رسانیGrid computing is moving into two ways. The Computational Grid focuses on reducing execution time of applications that require a great number of computer processing cycles. The Data Grid provides the way to solve large scale data management problems. Data intensive applications such as High Energy Physics and Bioinformatics require both Computational and Data Grid features. Job scheduling in Grid has been mostly discussed from the perspective of computational Grid. However, scheduling on Data Grid is just a recent focus of Grid computing activities. In Data Grid environment, effective scheduling mechanism considering both computational and data storage resources must be provided for large scale data intensive applications. In this paper, we describe new scheduling model that considers both amount of computational resources and data availability in Data Grid environment. We implemented a scheduler, called Chameleon, based on the proposed application scheduling model. Chameleon shows performance improvements in data intensive applications that require both large number of processors and data replication mechanisms. The results achieved from Chameleon are presented .
![ارزیابی اثر بخشی سیستم های اداری-مالی[taliem.ir]](https://taliem.ir/wp-content/uploads/ارزیابی-اثر-بخشی-سیستم-های-اداری-مالیtaliem.ir_.jpg)
ارزیابی مالی و اثر بخشی سیستم های اداری-مالی
اطلاع رسانیتوسعه اقتصادی کشورها و نیاز به حسابرسی سالانه صورت های مالی شرکت ها باعث شده است تا فعالیت های حسابرسی گسترش یابد.

